Natural Vegetation| Natural Vegetation of India| Types of natural vegetation in India
What is Natural Vegetation?
Natural vegetation refers to a plant community, which
has grown naturally without human aid and has been left undisturbed by humans for a long time.
Natural Vegetation in India MCQ's click HERE
Natural vegetation grows naturally and follows the climatic variables.
- Due to a variety of climates, a wide range of natural vegetation grows in India. - A study of the distribution of the forests in India reveals that there is a marked relation between the rainfall zones and their belts of natural vegetation
This is termed virgin vegetation.
Thus, cultivated crops and fruits, orchards form part of vegetation but not natural vegetation
virgin vegetation
The virgin vegetation, which are purely Indian are known as endemic or indigenous species but those
which have come from outside India are termed as exotic plants.
What is flora and fauna?
The term flora is used to denote plants of a particular region or period. Similarly,
the species of animals are referred to as fauna.
This huge diversity in flora and fauna kingdom is due to the following factors
(i) Relief: Land, Soil
Land: The nature of land influences the type of vegetation.
If the land is level and fertile, it is mainly used for farming.
If the land is uneven then grassland and woodlands develop over it.
Soil: Different types of soil are fit for different types of vegetation.
For example; sandy soil is fit for cactus and thorny bushes,
while wet and marshy soil is fit for mangrove vegetation.
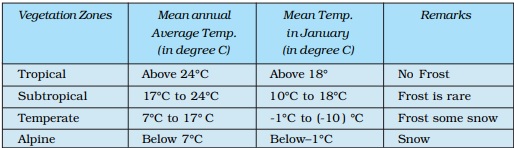
(ii) Climate: Temperature, Photoperiod(Sunlight), Precipitation,Temperature
Temperature and Humidity: determine the character and extent of vegetation.
- an area with high temperature and high humidity supports evergreen forest,
- an area with high temperature and low humidity supports thorny bushes.
Photoperiod (Sunlight): Photoperiod depends on latitude, altitude, season and duration of the day. Trees grow faster in summer because of the longer photoperiod.
Precipitation: If an area gets heavy rainfall, it is suitable for the growth of dense vegetation. On the other hand, an area with scanty rainfall is suitable for thorny bushes.
Characteristics of vegetation Zones Table
TYPES OF VEGETATION
Types of natural vegetation in India
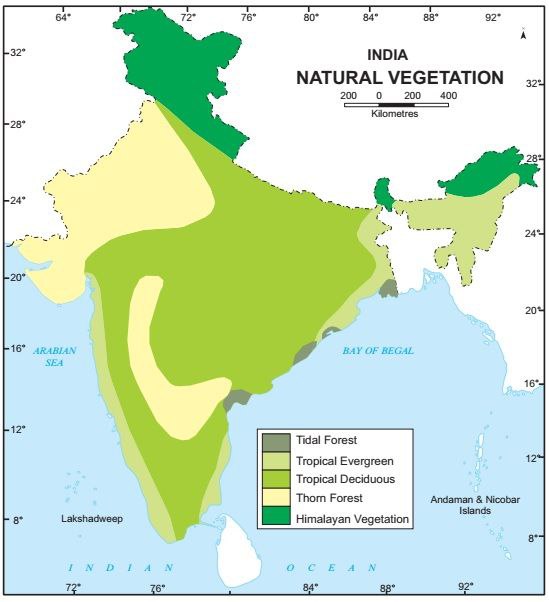
The following major types of vegetation may be identified in India
(i) Tropical Evergreen Forests
(ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests
(iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
(iv) Mountain Forests
(v) Mangrove Forests
1. Tropical Evergreen Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests are restricted to heavy rainfall areas of the Western Ghats and the island groups of
Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar, upper parts of Assam and Tamil Nadu coast.
They are at their best in areas having more than 200 cm of rainfall with a short dry season.
The trees reach great heights up to 60 metres or even above.
Since the region is warm and wet throughout the year, it has luxuriant vegetation
of all kinds: trees, shrubs and creepers giving it a multilayered structure.
There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves.
As such, these forests appear green all year round.
Important trees of Tropical Evergreen Forests
Some of the commercially important trees of this forest are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona.
Animals found in Tropical Evergreen forests
The common animals found in these forests are elephants, monkeys, lemurs and deer.
One-horned rhinoceroses are found in the jungles of Assam and West Bengal.
Besides these animals, plenty of birds, bats, sloths, scorpions and snails are also found in these jungles.
2. Tropical Deciduous Forests
Tropical Deciduous Forests are the most widespread forests of India.
They are also called monsoon forests and spread over the region receiving rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm.
Trees of this forest type shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in dry summer.
On the basis of the availability of water, these forests are further divided into moist and dry deciduous.
(a) moist tropical deciduous forest:
The moist tropical deciduous forest is found in areas receiving rainfall between 200 and 100 cm.
These forests exist, therefore, mostly in the eastern part of the country: northeastern states, along the foothills of the
Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Odisha and Chhattisgarh, and on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats.
Teak is the most dominant species of this forest. Bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair, kusum,
arjun and mulberry are other commercially important species.
(b) dry deciduous forests
The dry deciduous forests are found in areas having rainfall between 100 cm and 70 cm.
These forests are found in the rainier parts of the Peninsular plateau and the plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
There are open stretches, in which teak, sal, peepal and neem grow.
A large part of this region has been cleared for cultivation and some parts are used for grazing.
Animals found in tropical deciduous forests
In tropical deciduous forests, the common animals found are lions, tigers, pigs, deer and elephants.
A huge variety of birds, lizards, snakes and tortoises are also found here.
3. Thorn Forests and Scrubs
The Thorn Forests and Scrubs are found In regions with less than 70 cm of rainfall.
Thorn Forests and Scrubs natural vegetation consists of thorny trees and bushes.
Places of Thorn Forests and Scrubs
This type of vegetation is found in the north-western part of the country, including semi-arid
areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana.
Plants found in Thorn Forests and Scrubs
Acacias, palms, euphorbias and cacti are the main plant species.
Trees are scattered and have long roots penetrating deep into the soil in order to get moisture.
The stems are succulent to conserve water.
Leaves are mostly thick and small to minimise evaporation.
These forests give way to thorn forests and scrubs in arid areas.
Animals in Thorn Forests and Scrubs
In these forests, the common animals are rats, mice, rabbits,
fox, wolf, tiger, lion, wild ass, horses and camels.
4. Mountain Forests
Mountain Forests: In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with
increasing altitude leads to the corresponding change in natural vegetation.
As such, there is a succession of natural vegetation belts in the same order as we
see from the tropical to the tundra region.
The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 and 2000 metres.
Evergreen broad-leaf trees, such as oaks and chestnuts predominate.
Between 1500 and 3000 metres, temperate forests containing coniferous trees, like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar, are found.
These forests cover mostly the southern slopes of the Himalayas, places having high altitudes in
southern and north-east India.
At higher elevations, temperate grasslands are common.
At high altitudes, generally, more than 3,600 metres above sea level, temperate forests and grasslands give way to the Alpine vegetation.
Trees in Mountain Forests
Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees of these forests.
However, they get progressively stunted as they approach the snow line.
Ultimately, through shrubs and scrubs, they merge into the Alpine grasslands.
These are used extensively for grazing by nomadic tribes, like the Gujjars and the Bakarwals.
At higher altitudes, mosses and lichens form part of tundra vegetation.
Animals in Mountain Forests
The common animals found in these forests are Kashmir stag, spotted dear, wild sheep, jack rabbit,
Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels,
Shaggy horn wild ibex, bear and rare red panda, sheep and goats with thick hair.
6. Mangrove Forests
Mangrove Forests: The mangrove tidal forests are found in the areas of coasts influenced by tides.
Mud and silt get accumulated on such coasts.
Dense mangroves are the common varieties with roots of the plants submerged under water.
The deltas of the Ganga, the Mahanadi, the Krishna, the Godavari and the Kaveri are covered by such vegetation.
In the GangaBrahmaputra delta, Sundari trees are found, which provide durable hard timber.
Plants and trees in Mangrove Forests
Palm, coconut, keora, agar, etc., also grow in some parts of the delta.
Animals in Mangrove Forests
Royal Bengal Tiger is a famous animal in these forests. Turtles, crocodiles, gharials and snakes are also found in
these forests.
Natural Vegetation FAQ's
What is natural vegetation?
Natural vegetation refers to a plant community, which has grown naturally without human aid and has been left undisturbed by humans for a long time.
What are the uses of natural vegetation?
Vegetation converts solar energy into biomass and forms the base of all food chains. It influences the energy balance at the earth's surface and within the atmospheric boundary layer, often mitigating extremes of local climate. Vegetation releases oxygen and sequesters carbon
What are the 3 natural vegetation types?
What are the 5 natural vegetation types?
What are the 5 types of vegetation?
(i) Tropical Evergreen Forests
(ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests
(iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
(iv) Mountain Forests
(v) Mangrove Forests
What are the 6 natural vegetation types?
(1) Tropical Evergreen Rain Forests,
(2) Deciduous or Monsoon Type of Forests,
(3) Dry Deciduous Forests and Scrubs,
(4) Semi Desert and Desert Vegetation,
(5) Tidal or Mangrove Forests and
(6) Mountain Forests
What are the 5 types of vegetation?
(i) Tropical Evergreen Forests (ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests (iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs (iv) Mountain Forests (v) Mangrove Forests
What are the 3 natural vegetation types?
Forest, grassland, and shrubs are the three main classifications
What are the 7 vegetation zones?
Alpine and arctic tundra and ice. Boreal forest. Temperate deciduous forest and subtropical evergreen forest. Temperate grasslands. Desert and semidesert. Tropical deciduous forest and savanna. Tropical rainforest.
What are the 6 types of forests?
Tropical evergreen forests, Tropical deciduous forests, Tropical thorn forests, Montane forests, and Swamp forests
What are planted vegetation?
Planted Vegetation is the the plant cover of an area that is grown by people
What is wildlife vegetation?
Wildlife vegetation is the wildlife is the fauna of a region
Is Grass a vegetation?
The predominant vegetation consists of grasses and forbs
What is importance of vegetation?
Vegetation converts solar energy into biomass and forms the base of all food chains. It influences the energy balance at the earth's surface and within the atmospheric boundary layer, often mitigating extremes of local climate. Vegetation releases oxygen and sequesters carbon















No comments:
Post a Comment